20zr暑期AB班十连测day9



A
zhq切掉了
u和v xor起来最大那么如果不他在两条链上答案就就是u和vxor起来的答案
那么相当于只有两条链啊,对于包括u和v的两条链,那么我们就可以考虑这两个链不加入,然后其他的点都加进去,然后随着链下降我们会加入一些新点,这都问题不大
O(nw)极其好写
code
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<map>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int MAXM = 1e6 + 7;
const int MAXN = 5e5 + 7;
map<ll, int> mp;
int n, fa[MAXN], ccnt, ansu, ansv;
int home[MAXN], nxt[MAXM], to[MAXM];
ll a[MAXN], ans[MAXN], Nans, tmpans;
inline void ct(int x, int y) {
ccnt++;
nxt[ccnt] = home[x];
home[x] = ccnt;
to[ccnt] = y;
}
const int MAXT = 1e7 + 7;
struct rec {
int ch[MAXT][2];
int siz[MAXT];
int T, root;
inline void ins(ll V) {
int u = root;
for(int i = 60; i >= 0; --i) {
int t = (V >> i) & 1;
if(!ch[u][t])ch[u][t] = ++T;
siz[u]++;
u = ch[u][t];
}
siz[u]++;
return ;
}
inline void del(ll V) {
int u = root;
for(int i = 60; i >= 0; --i) {
int t = (V >> i) & 1;
siz[u]--;
u = ch[u][t];
}
siz[u]--;
return;
}
inline ll query(ll V) {
ll qwq = 0;
int u = root;
for(ll i = 60; i >= 0; --i) {
int t = V >> i & 1;
if(!ch[u][t ^ 1])u = ch[u][t];
else if(siz[ch[u][t ^ 1]] >= 1)
u = ch[u][t ^ 1], qwq |= (1ll << i);
else u = ch[u][t];
}
return qwq;
}
} T2;
inline void init() {
Nans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ll tmp = T2.query(a[i]);
T2.ins(a[i]);
if(tmp > Nans) {
ansu = i;
ansv = mp[tmp ^ a[i]];
Nans = tmp;
}
}
// printf("%d %d %d?\n", Nans, ansu, ansv);
return ;
}
inline void add(int u, int F) {
tmpans = max(T2.query(a[u]), tmpans);
T2.ins(a[u]);
for(int i = home[u]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = to[i];
if(v == F)continue;
add(v, u);
}
}
int tp, tk[MAXN];
inline void solve(int x) {
memset(T2.ch, 0, sizeof(T2.ch));
T2.T = 1;
T2.root = 1;
memset(T2.siz, 0, sizeof(T2.siz));
tp = 0;
while(x != 0) {
tk[++tp] = x;
x = fa[x];
}
tmpans = 0;
for(int i = tp; i >= 1; --i) {
int u = tk[i];
// printf("!%d \n", u);
ans[u] = tmpans;
for(int k = home[u]; k; k = nxt[k]) {
int v = to[k];
if(v == tk[i - 1] || v == fa[u])continue;
// printf("%d?\n", v);
add(v, u);
//插入顺便更新答案qwq
}
tmpans = max(tmpans, T2.query(a[u]));
T2.ins(a[u]);
}
return ;
}
inline void solve2() {
Nans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ans[i] = Nans;
T2.ins(a[i]);
Nans = max(Nans, T2.query(a[i]));
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
}
int main() {
// freopen("test.in", "r", stdin);
scanf("%d", &n);
bool flg = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &fa[i]);
if(fa[i] != i - 1)flg = 0;
ct(i, fa[i]);
ct(fa[i], i);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
mp[a[i]] = i;
}
if(flg) {
solve2();
return 0;
}
memset(ans, -1, sizeof(ans));
init();//get u,v
solve(ansu);
// puts("--------");
solve(ansv);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
if(ans[i] != -1)printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
else printf("%lld\n", Nans);
return 0;
}

B
构造
角上X<=4
边上加角上我们可以最多的能放就放放出答案
X+Y<=4+R-y/2
就是小于等于2* R/2 +2* C/2 +4
点数小于等于边数-1
总边数减去黑格删去的边数角落边界和内部黑格删去的不同
x+2Y+3Z<=(R-1)(C-1)
3(X+Y+Z)<=2R/2+2C/2+4
当然这个上界可能取不到
n=3k 上界是n^2/3
n=6k+1,6k+5 n^2+2/3
n=6k+2,6k+4 n^2+1/3
如果9要取到等号边界要放满5个格子...
然后根据连通性我们边界上都要是
然后偶数就可以...由题解构造...
先定下中间的部分,再一步步扩张,是构造的基本思路
间行种植可以帮助我们解决扩张
而中间的部分...只能自己慢慢试了....
n=6k
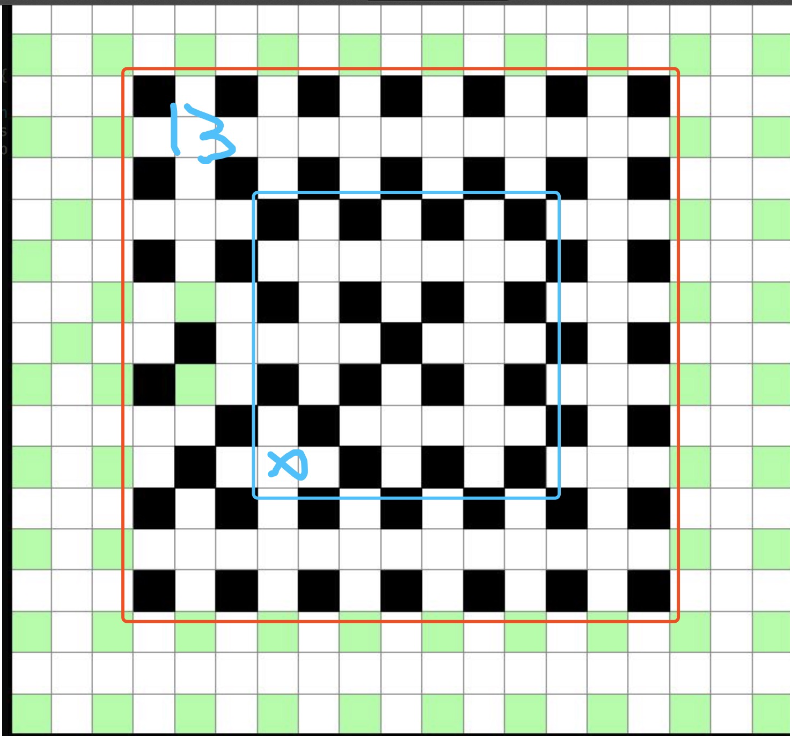
n=6k+1
n=6k+2
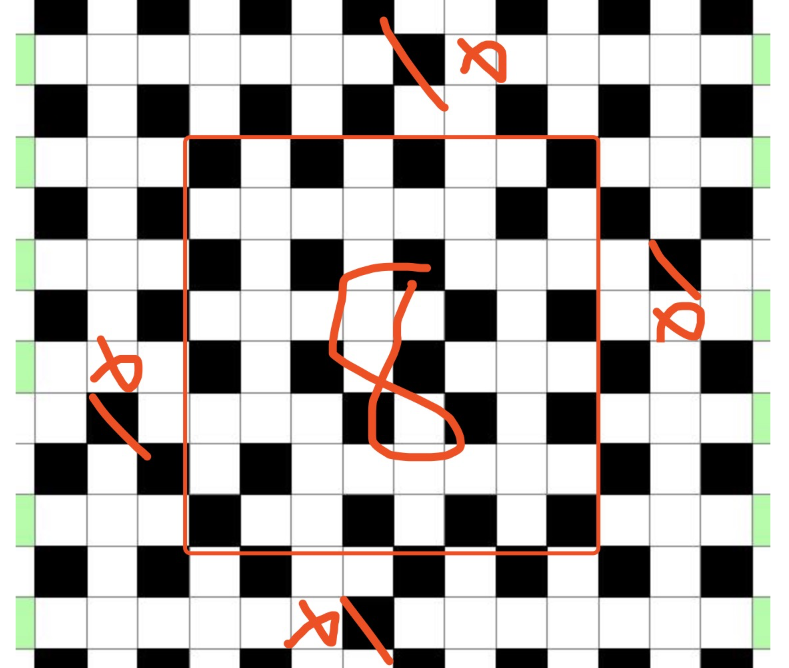
n=6k+3
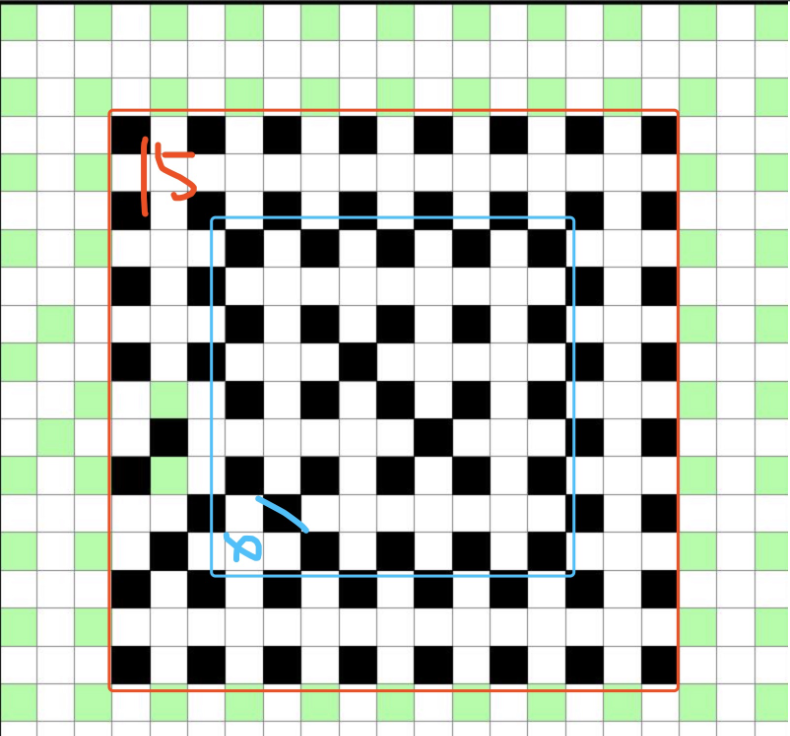
n=6k+4
n=6k+5
当然最简单的6k也可以使用
其实这个启发我们网格构造题可以考虑从中间起手扩展
但是中间的起手一定要花大点的...两倍差不多
C
考虑把所有d压成一个d维向量S记在每个点上....
然后对于一个向量,他的出边就是随机一个权值然后*该点向量然后再
对于一个点,他的最小割就是所有入边形成的线性空间的秩...就是基底
那会发现最小割大小不超过3,则构成这个点向量的秩数就不超过3...
求秩就是求线性基的大小,所有的入边构成一个线性基,然后考虑用这个线性基去求这个向量的秩数...
然后我们不要每次拿所有的入边去做,每次削成一个线性基,然后就解决了
首先秩小于等于最小割啊....另外我们由于随机所以大概率对吗
其实就是入边是一些不同的线性组合构成的就大概率能保证这个点也是对的...
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 7;
const int MAXM = 1e6 + 7;
const int P = 998244353;
int n, K, m;
int vis[MAXN], home[MAXN], nxt[MAXM], to[MAXM], first[MAXN], ccnt;
int c[MAXN], que[MAXM], d[MAXN], ans[MAXN];
inline void ct(int x, int y) {
ccnt++;
nxt[ccnt] = home[x];
home[x] = ccnt;
to[ccnt] = y;
}
inline void ct2(int x, int y) {
ccnt++;
nxt[ccnt] = first[x];
first[x] = ccnt;
to[ccnt] = y;
}
inline void dfs(int u) {
vis[u] = 1;
for(int i = home[u]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = to[i];
if(vis[v])continue;
dfs(v);
}
}
inline ll ksm(ll x, int y) {
ll ans = 1;
while(y) {
if(y & 1)ans = ans * x % P;
x = x * x % P;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
struct rec {
int a[12];
inline rec &operator+=(const rec &x) {
for(int i = 0; i <= K; ++i) {
a[i] = (a[i] + x.a[i]) % P;
}
return *this;
}
inline rec operator+(const rec &x) const {
rec c = *this;
c += x;
return c;
}
inline rec &operator*=(const ll &x) {
for(int i = 0; i <= K; ++i) {
a[i] = (1ll * x * a[i]) % P;
}
return *this;
}
inline rec operator *(const int &x) const {
rec c = *this;
c *= x;
return c;
}
} b[MAXN];
struct _list {
int n;
vector<rec> V;
inline int gs() {
int n = V.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)b[i] = V[i];
//拿b消元才行
for(int i = n; i < max(n, K); ++i) {
for(int j = 0; j < K; ++j) {
b[i].a[j] = 0;//init
}
}
n = max(n, K);
//个数和列数取最大
V.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
c[i] = 0;
}
for(int i = 0; i < K; ++i) {
if(!b[i].a[i]) {
//如果这个对角线是空的...
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if(!c[j] && b[j].a[i]) {
swap(b[i], b[j]);
//交换两行
//就是我们之后的的有一个没有被动过的这个位置有数
break;
}
}
}
if(!b[i].a[i])continue;
c[i] = 1;
V.push_back(b[i]);
//加入这一行
//说明这一行有东西啊
int t = P - ksm(b[i].a[i], P - 2);
//求下逆
for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if(j != i && b[j].a[i]) {
//高斯消元
int c = 1ll * t * b[j].a[i] % P;
//乘上这个再加就可以使他变为0
b[j] = b[j] + b[i] * c;
//一行加一列
}
}
}
return V.size();
}
} a[MAXN];
inline int mrand() {
return (rand() << 16)^rand() + rand();
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
ct(u, v);
ct2(v, u);
}
dfs(1);
// puts("qwq");
for(int u = 1; u <= n; ++u) {
for(int i = first[u]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = to[i];
if(vis[v])
d[u]++;
}
}
// for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
// printf("%d\n", d[i]);
srand(114514);
for(int i = home[1]; i; i = nxt[i])++K;
// b[1].a[1] = 1;
// b[1] *= 2;
// b[1] += b[1];
// printf("%d\n", b[1].a[1]);
// printf("%d\n", K);
int N = 0, head = 1, tail = 1;
que[tail] = 1;
while(head <= tail) {
int u = que[head];
// printf("%d*&\n", u);
++head;
if(u != 1)
ans[u] = a[u].gs();
for(int i = home[u]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = to[i];
rec t;
for(int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
t.a[k] = 0;
if(u == 1)
t.a[N++] = 1;//初始基底
else {
for(int i = 0; i < a[u].V.size(); ++i) {
t = t + a[u].V[i] * (mrand() % P);
}
}
a[v].V.push_back(t);
d[v]--;
if(!d[v])que[++tail] = v;
//拓扑
}
}
for(int i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
强烈推荐弹丸论破
尤其是狛枝凪斗的希望教...