CF521E Cycling City

IOI2020集训队作业
已经预感不能再像现在这样刷题了...唉,准备开学吧
- 给定一张 个点 条边的无向简单图。
- 问图中能否找到两个点,满足这两个点之间有至少三条完全不相交的简单路径。
- ,图不保证连通。
这个题真的是构造题啊....因为我们只需要构造出一种通用的情境满足题意就行了QAQ,所以图论好像大部分这样裸的都是构造啊
怎么构造呢?先观察样例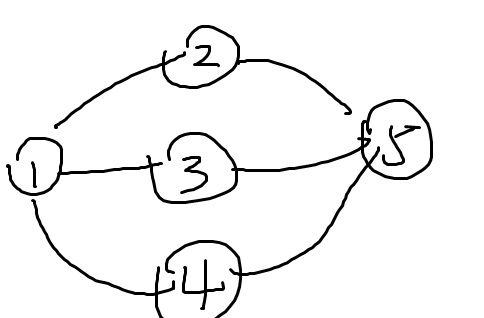
不难发现一个合法的一对点一定是两个环重复的部分
这个显然充分,必要性....因为是无向图好像是一样的吧QAQ....
所以问题变成了找有没有这样被两环覆盖的,经典问题
考虑先建出dfs树,然后对于一条非树边暴力覆盖到另一端点上所有点,然后直到某一刻有一个点被覆盖了2次,说明他是两环重复了
我们覆盖时也并不直接记次数,而是记哪条非树边覆盖他
不妨令 dfs 树作为生成树,令 b 为 a 的祖先,d 为 c 的祖先,b 的深度比 d 的深度浅。
不需要任何分类讨论,画个图就很容易明白,三条路径铁定就是:
- d -> lca(a, c)
- d -> b -> a -> lca(a, c)
- d -> c -> lca(a, c)
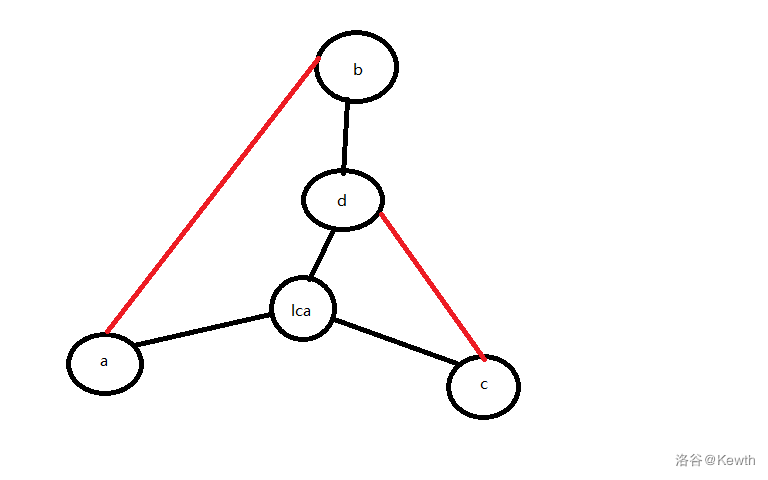
这样就好了所以我们还差个复杂度分析/jk
你会惊人的发现每个点最多被这样暴力跳过一次,因为如果暴力跳过两次就相当于找到答案了
所以复杂度是线性的
code:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#define ll long long
#define CT const int&
using std::reverse;
const int MAXN = 6e5 + 7;
int n, m, ccnt;
int home[MAXN], nxt[MAXN], to[MAXN];
bool vis[MAXN], ins[MAXN];
int fa[MAXN], deep[MAXN];
int cx[MAXN], cy[MAXN];
int LCA(int x, int y) {
while(deep[x] > deep[y])x = fa[x];
while(deep[y] > deep[x])y = fa[y];
while(x != y)x = fa[x], y = fa[y];
return x;
}
int tmp[MAXN], tp;
inline void ct(CT x, CT y) {
ccnt++;
nxt[ccnt] = home[x];
home[x] = ccnt;
to[ccnt] = y;
}
void addpath(int x, int y) {
while(x != y) {
tmp[++tp] = x;
x = fa[x];
}
tmp[++tp] = y;
}
void print() {
printf("%d ", tp);
for(int i = 1; i <= tp; ++i) {
printf("%d ", tmp[i]);
}
puts("");
tp = 0;
}
#define swap(x,y) (x^=y^=x^=y)
inline void get(int a, int b, int c, int d) {
if(deep[b] > deep[d]) {
swap(a, c);
swap(b, d);
}
int e = LCA(a, c);
puts("YES");
//就是对应了上图画的三种情况啊
addpath(e, d);
reverse(tmp + 1, tmp + tp + 1);
print();
addpath(d, b);
addpath(a, e);
print();
tmp[++tp] = d;
addpath(c, e);
print();
exit(0);
}
inline void dfs(int u) {
deep[u] = deep[fa[u]] + 1;
vis[u] = ins[u] = 1;
//printf("%d?\n", u);
for(int i = home[u]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = to[i];
if(v != fa[u]) {
if(!vis[v]) {
fa[v] = u;
dfs(v);
} else if(ins[v]) {
for(int x = u; x != v; x = fa[x]) {//这一步线性
if(cx[x] && cy[x]) {
get(cx[x], cy[x], u, v);//这两个路径交点
} else {
cx[x] = u;
cy[x] = v;//标记一整个路径
}
}
}
}
}
ins[u] = 0;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1, u, v; i <= m; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
ct(u, v);
ct(v, u);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)if(!vis[i])dfs(i);
puts("NO");
return 0;
}